More Great Ways in Which Songwriters Have Used First-Inversion Chords
Learn some compositionally effective ways in which first-inversion chords have been used in popular music.
All the latest guitar news, interviews, lessons, reviews, deals and more, direct to your inbox!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Last month, we looked at several stylistically diverse examples of musically appealing ways in which famous bands, recording artists and songwriters have used first-inversion chords (specifically triads) in some of their most celebrated songs. First-inversion means with the chord’s third being the lowest note in the voicing, or “in the bass.” I’d now like to continue with this worthwhile topic and cite a few more examples of compositionally effective ways in which first-inversion chords have been used in popular music.
One good, smooth-sounding way to use a first-inversion major chord is as a “filler” between the I and IV chords in a major key. This creates the feeling of a chord change without actually changing the harmony of the previous chord. Three famous acoustic guitar-driven examples that immediately come to mind are the intro and verse to “Don’t Follow” by Alice in Chains, the outro section of “Patience” by Guns N’ Roses and the verses to “Thinking Out Loud” by Ed Sheeran; all of which repeatedly go from an open D chord to D/F# to G (the first two songs performed on guitars tuned down a half step), using the common voicings illustrated in FIGURE 1. (The low F# note, which is the third of the D chord, may be conveniently fretted with the thumb.) The famous piano ending to “Layla” by Derek and the Dominos, elegantly performed by Jim Gordon, features the same three-chord loop, played down a whole step, in the key of C. FIGURE 2 shows pleasant-sounding guitar voicings for the progression in that key, as well as standard ways to finger them in the other important guitar keys of G, A and E major.
You could, of course, just use first-inversion chords sort of randomly or chromatically — as Pearl Jam’s Eddie Vedder did to great effect in “Better Man” — using the movable shape illustrated in FIGURE 3, and fingerpicking the strings to obtain the sparse, open-sounding voicing. Notice how much musical warmth and weight the low third in the bass provides.
A more dramatic way to use a first-inversion chord is to create a chromatic bass-line “walk up” from the V chord of a major key to the relative minor, or vi minor, chord, with the insertion of a secondary dominant with the third in the bass. A good, well-known example of this can be found in the pre-chorus of Oasis’ mid-Nineties hit “Don’t Look Back in Anger,” where the progression, which is in the key of C overall, goes from an open G5 chord to an unusual and clever voicing of E7/G#. This utilizes the open D string in conjunction with three fretted notes, to Am, as is FIGURE 4.
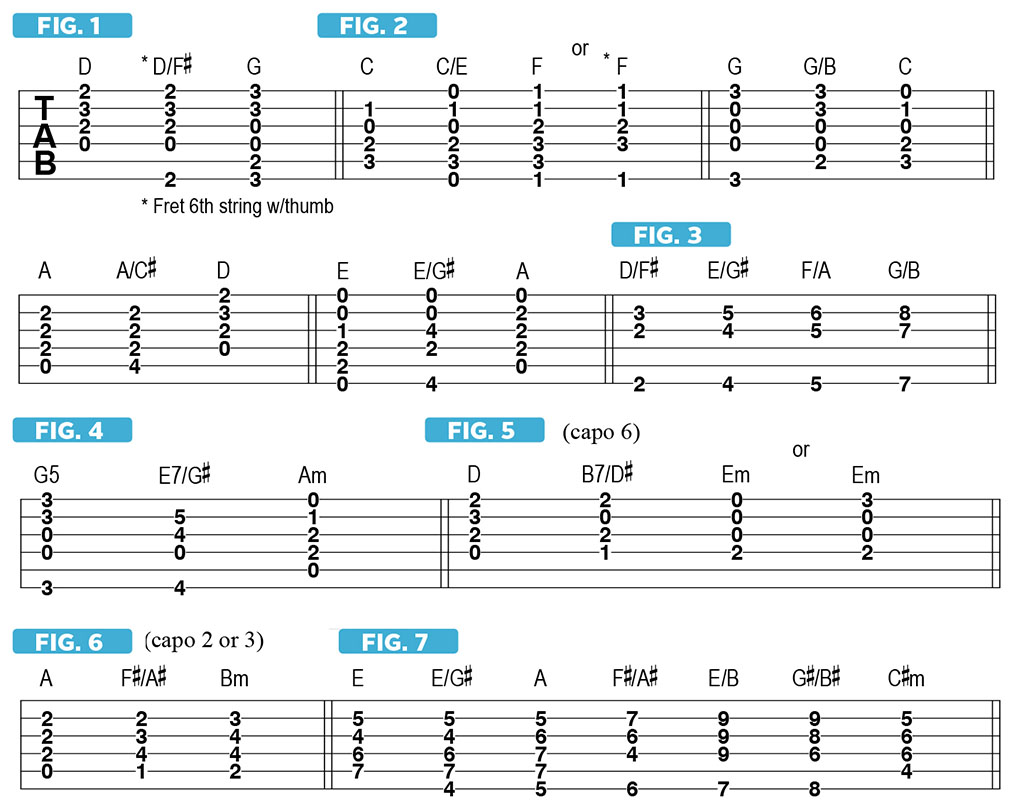
The late Jeff Buckley employed this same “tug on my heart strings” move near the end of each verse in his impassioned cover of the Leonard Cohen song “Hallelujah;” for which the guitarist, using a capo at the sixth fret, plays an open D chord, followed by B7/D#, which begs compellingly for a resolution to Em, as is FIGURE 5. Jon Bon Jovi’s piano-driven cover of the song, performed in the key of B, features the same move, in this case from F# to Eb/G to G#m (that second chord, for you theory sticklers, is technically called D#/Fₓ — “D sharp over F double sharp”). Interestingly, in Cohen’s original reading of the song, which he recorded in the key of C, the songsmith follows the same basic progression but doesn’t make use of the first-inversion with the secondary dominant chord, in this case E7. So it’s essentially the same three chords as those cited earlier in “Don’t Look Back in Anger,” minus the G# bass note in the E7 chord.
That other great American songwriter, James Taylor, employed this first-inversion, secondary-dominant move to the relative minor chord in some of his classic songs, such as “Carolina in My Mind,” “Shower the People” and “Your Smiling Face,” using voicings like those illustrated in FIGURES 6 and 7. In the latter example, JT masterfully chains together root-position, first-inversion and second-inversion triads to create a chromatic bass climb that’s pretty much the opposite of what Paul McCartney did in the verses to “Maybe I’m Amazed,” which we looked at last time.
Senior Music Editor "Downtown" Jimmy Brown is an experienced, working guitarist, performer and private teacher in the greater NYC area whose professional mission is to entertain, enlighten and inspire people with his guitar playing and lessons.
All the latest guitar news, interviews, lessons, reviews, deals and more, direct to your inbox!
Over the past 30 years, Jimmy Brown has built a reputation as one of the world's finest music educators, through his work as a transcriber and Senior Music Editor for Guitar World magazine and Lessons Editor for its sister publication, Guitar Player. In addition to these roles, Jimmy is also a busy working musician, performing regularly in the greater New York City area. Jimmy earned a Bachelor of Music degree in Jazz Studies and Performance and Music Management from William Paterson University in 1989. He is also an experienced private guitar teacher and an accomplished writer.

